Updated March 17, 2025 Authored by Dr. Chris Cloney and Jon Barrett of Dust Safety Science
Combustible dust might sound harmless, but under the right conditions, it can lead to catastrophic explosions with devastating consequences. This hidden hazard lurks in unsuspecting places. But what is combustible dust, and how can it be managed effectively to ensure safety?
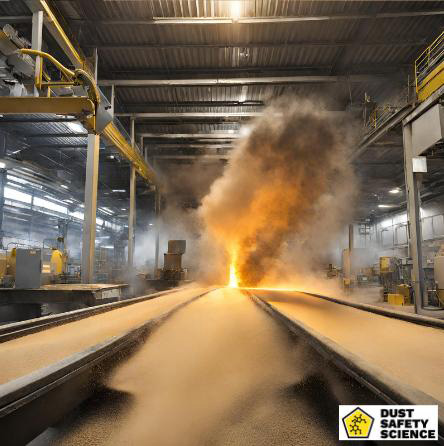

Combustible dust is a serious threat in various industries, often underestimated until an explosion occurs. Understanding combustible dust is crucial, as neglecting it can lead to severe consequences, including:
-
- Fires and explosions
- Injuries and fatalities
- Equipment and property damage
- Regulatory fines and business shutdowns
This comprehensive guide is designed to shed light on what combustible dust is and, more importantly, how to effectively manage it to ensure safety in the workplace from dust explosions.
Key Takeaways:
-
- Regulatory Compliance: To meet legal requirements and avoid fines.
- Asset Protection: To safeguard equipment and infrastructure from a dust explosion.
- Business Continuity: To prevent costly production interruptions from a dust explosion.
- Environmental Responsibility: To avoid environmental damage and associated liabilities from a dust explosion.
Don’t let the hidden dangers of combustible dust catch you off guard.
INDEX
What is Combustible Dust?
Combustible dust refers to finely divided solid particles that are prone to ignition when suspended in the air. These particles can originate from various materials and industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and chemical processing. In this section, we’ll delve deeper into what qualifies dust as combustible, the technical definitions, and why it poses a significant risk and primary hazard for dust explosions.
Characteristics of Combustible Dust:
- Particle Size: Fine particles (smaller than 420 microns) are more likely to ignite.
- Concentration: Dust clouds must reach a specific concentration to become combustible.
Chemical Composition: Some materials have inherently flammable properties.
Understanding these characteristics is vital for identifying and managing the risks associated with combustible dust, ensuring workplace safety and compliance from dust explosions.
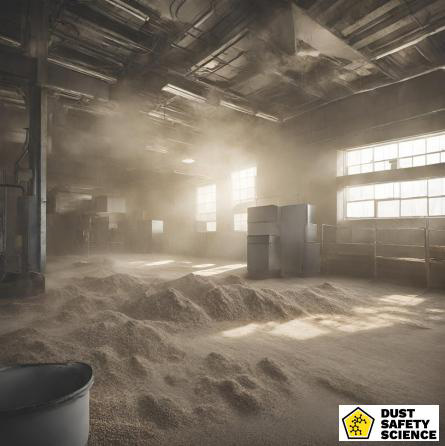

Types of Combustible Dust
Different industries produce various types of combustible dust, each with unique risks:
1. Organic Dust
Organic dust particles are derived from natural solid materials such as wood, food production, and agricultural products such as grains, sugar, powdered milk, and flour. Most solid organic materials have the potential to produce fine, flammable dust when processed, handled, or transported.
Organic dust particles are a hazard risk due to their ability to form explosive dust clouds when suspended in the air and, as a result, can cause a dust explosion. Implementing preventive measures in industries like woodworking, food processing, and agriculture, which create dust, can prevent a catastrophic explosion.
2. Metal Dust
Metal dust comprises of finely divided, solid tiny particles of metals like aluminum, zirconium, and magnesium. These metals are known for their combustible nature, especially when reduced to fine dust. The ignition of metal combustible dust can result in intense fires and dust explosions, making proper containment and control imperative in industries like metalworking, metal processing, and aerospace manufacturing.
3. Chemical Dust
Chemical dust includes substances like coal dust and sulfur, which can be highly flammable and may cause a dust explosion when in particulate form. These fine particles and materials often pose additional challenges due to their chemical reactivity and the potential for toxic byproducts during combustion.
Managing chemical dust hazards to prevent a dust explosion is crucial in industries such as chemical manufacturing, mining, and energy production. If such a dust is suspended in the air in the right concentration, under certain conditions, it can become explosible.
By recognizing the distinct particles and characteristics, and risks associated with these solid material composed of organic substances and types of combustible dust, such as powdered milk, businesses can implement tailored safety measures, including dust control, ventilation, and employee training, to mitigate the potential for combustible dust explosions. Prioritizing safety not only protects workers but also ensures compliance with regulatory standards, ultimately safeguarding the integrity of your operations, from dust explosions.
Managing combustible dust effectively starts with the right knowledge.
Industries Affected by Combustible Dust
Industries that generate combustible dust face the looming threat of a dust explosion, but certain sectors are particularly susceptible to this explosion hazard concern. Understanding the industries creating combustible dust is vital for proactive risk management from a dust explosion.
Among the list of industries generating combustible dust and most prone to combustible dust issues include:
- Woodworking and sawmills – Wood dust is prevalent and is a significant hazard.
- Food processing, food production, and agricultural products – Sugar and flour dust pose significant risks.
- Chemical manufacturing facilities – Combustible dust explosions happen in handling materials, using abrasive blasting or screening dry materials like coal and sulfur are also an explosion hazard.
- Metalworking industry – Metal dusts like aluminum and magnesium can catch fire and explode.
Agriculture products and grain handling, pharmaceutical production, recycling facilities, and many others generate dust and also contend with combustible dust challenges.
By acknowledging the range of industries impacted, we emphasize the need for tailored safety measures, comprehensive training, and compliance to ensure the utmost protection for workers and assets in these high-risk environments from a dust explosion.
The Science of Combustible Dust
The Combustion Triangle, Square, and Pentagon
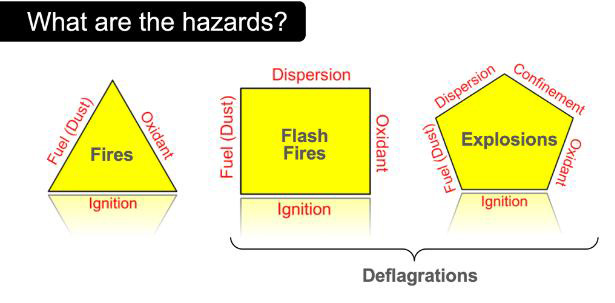
Elements Needed for Combustible Dust to Catch Fire
Understanding the combustion triangle is paramount when it comes to comprehending the factors that enable combustible dust to cause a fire and create a dust explosion. This essential concept revolves around three key elements:
- Fuel
- Oxygen
- An ignition source
First and foremost, combustible dust serves as the fuel component, encompassing finely divided materials like wood, sugar, or coal. Next, a sufficient oxygen supply must be present in the atmosphere. Lastly, the ignition source, and how dust ignites, which can be as simple as a spark, open flame, static electricity, or even heat generated from friction, bridges the gap between the fuel and oxygen, triggering combustion.
By grasping the technical definition and dynamics of the combustion triangle, industries can implement proactive measures to control these elements, effectively reducing the risk of a combustible dust catch fire and explode.
In addition to the familiar fire triangle of oxygen, heat, and fuel (the dust), the dispersion of dust particles in sufficient quantity and concentration can cause rapid combustion known as deflagration. If the event is confined by an enclosure such as a building, room, vessel, suspended ceilings, dust collectors, or process equipment, the resulting pressure rise may cause an explosion. These five factors (oxygen, heat, fuel, dispersion, and confinement) are known as the Dust Explosion Pentagon. If one element of the dust explosion pentagon is missing, an explosion cannot occur.
Factors Influencing Combustibility
Combustible dust varies, and several factors play a pivotal role in influencing the combustibility of dust. Understanding these factors is critical for hazard management and preventing a combustible dust explosion.
-
- Particle size is a key determinant, as smaller particles and finer particles, typically under 420 microns, possess a larger surface area, making them more prone to ignition when suspended in the air.
- Moisture content is equally vital, as it can either mitigate or exacerbate combustibility. Dust with low moisture content tends to be more volatile and easier to ignite, while higher moisture levels can dampen the risk.
- Concentration is another significant factor. When dust particles reach a critical concentration in the atmosphere, they can form an explosive cloud, dramatically increasing the potential for ignition.
By taking these factors into account and implementing effective control measures, industries can significantly reduce the risks associated with combustible dust incidents and preventing a primary explosion.
Empower your team with critical safety insights.
Explosive Dust Clouds
Explosive dust clouds represent a perilous hazard in various industries. Understanding how combustible dust can form these dangerous clouds is paramount for safety.
When fine particles of combustible dust become suspended in the air in a sufficient concentration and physical state, the particles can create a highly combustible mixture. When the dust ignites, and the dust catches fire, it may cause a combustible dust explosion.
The critical elements here are:
-
- The concentration of dust in the atmosphere (typically expressed as a dust-to-air ratio)
- The presence of an ignition source
When these factors align, even static electricity, open flames, or a tiny spark or heat source can trigger a catastrophic explosion. This phenomenon underscores the importance of meticulous dust control, ventilation, and ignition source management to prevent dusts suspended in air, and the formation of explosive clouds.
By proactively addressing these explosion pentagon factors, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of combustible dust-related incidents and prevent combustible dust explosions, ensuring worker safety.
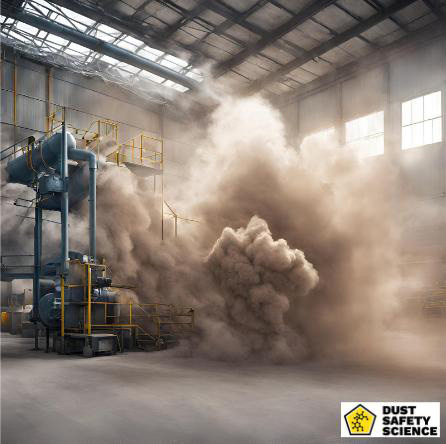

Risks Associated with Combustible Dust
Health Risks
Exposure to combustible dusts not only poses significant fire and explosion risks but also presents serious health hazards to workers. Inhalation of airborne dust particles can lead to a range of respiratory issues, from irritation and coughing to more severe conditions like pneumoconiosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Additionally, certain types of combustible dust, such as metal or chemical dust, may contain toxic substances that can result in acute or chronic poisoning. Skin and eye irritation are also common when workers come into contact with dust particles.
To mitigate these health risks, it’s crucial for industries that generate compostable dust, to:
- Implement robust dust control measures
- Prevent specks of dust suspended in the air
- Provide adequate personal protective equipment
- Ensure comprehensive training and awareness programs for employees
Prioritizing worker health enhances the safety and well-being of the workforce. It also aligns with combustible dust safety best practices, as it reflects a commitment to responsible and sustainable business practices.
Safety Risks
Safety risks stemming from combustible dusts, or a flash fire hazard, or an explosion hazard when suspended in air, are a matter of utmost concern across various industries.
The primary hazards are fire and explosions, which can result in catastrophic consequences. Combustible dust, when suspended in the air in sufficient concentrations, can ignite with alarming speed, often triggered by a spark, heat source, or hot surfaces. The resulting fires can be intense and destructive, endangering lives, causing injuries, and damaging property.
Moreover, combustible dust explosions in a confined space have the potential to unleash devastating shockwaves, leading to structural damage and secondary fires in an enclosed space.
It’s imperative for businesses to prioritize safety through comprehensive dust management, including dust control, ventilation, and employee training, to mitigate these risks effectively. This commitment to facility safety protects lives and assets and aligns with combustible dust safety strategies. Remember, responsible businesses gain recognition for their dedication to minimizing safety hazards.
Real-World Incidents
Case studies of accidents or incidents involving combustible dust. Real-world incidents involving combustible dust have left a trail of destruction and underscore the critical importance of proactive safety measures.
Several notable case studies serve as stark reminders of the potential hazards. One such incident occurred at a sugar refinery in 2008, where a massive dust explosion in an enclosed space, claimed lives and caused extensive damage. Similarly, a grain elevator explosion in 2011 and enclosed space resulted in tragic consequences due to combustible grain dust. These incidents and others serve as valuable lessons, emphasizing the need for rigorous dust management, employee training, and compliance.
By examining these real-world examples, with agricultural products and dust present, businesses can better grasp the gravity of combustible dust risks and take measures to prevent such devastating incidents.
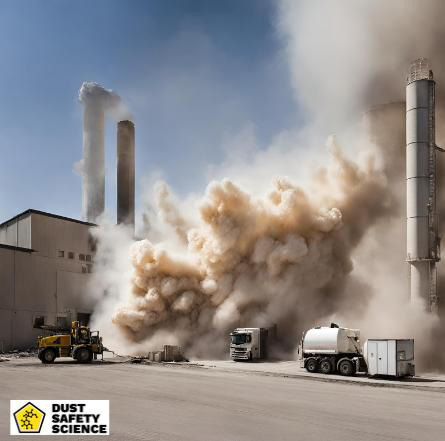

Are you aware of the dangers of combustible dust and how to handle it safely?
Regulations and Compliance for Combustible Dust:
OSHA Guidelines
Navigating the complexities of combustible dust hazards is made more manageable with the guidance of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
OSHA has provided comprehensive guidelines that define combustible dust to help businesses mitigate the risks associated with combustible dust. These guidelines encompass key aspects such as hazard recognition, assessment, and control measures. They emphasize the importance of conducting thorough dust hazard analyses, implementing preventive measures, and maintaining effective housekeeping practices.
By adhering to OSHA’s health administration guidelines, businesses can not only ensure the safety of their employees but also remain compliant with regulatory standards. This commitment to safety and compliance aligns seamlessly with Combustible Dust safety strategies, as responsible businesses are recognized and trusted for their dedication to protecting lives and maintaining best practices in their industries.
NFPA Standards
Navigating the intricate landscape of combustible dust safety is made more accessible through the guidelines set forth by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). The NFPA has established essential standards, including NFPA 652 “Standard on the Fundamentals of Combustible Dust” and the following standards:
-
- NFPA 61: Standard for the Prevention of Fires and Dust Explosions in Agricultural and Food Processing Facilities
- NFPA 484: Standard for Combustible Metals
- NFPA 654: Standard for the Prevention of Fire and Dust Explosions from the Manufacturing, Processing, and Handling of Combustible Particulate Solids
- NFPA 655: Standard for Prevention of Sulfur Fires and Explosions
- NFPA 664: Standard for the Prevention of Fires and Explosions in Wood Processing and Woodworking Facilities
These standards encompass crucial aspects such as hazard identification, risk assessment, and control measures. They stress the importance of conducting dust hazard analyses, establishing preventative measures from an ignition source and adopting robust housekeeping practices.
By adhering to the NFPA’s standards, companies can not only ensure the well-being of their workforce but also achieve compliance with industry best practices that create dust. This commitment to safety and industry standards aligns harmoniously with combustible dust safety strategies, as businesses that prioritize responsible practices and adherence to guidelines garner recognition and trust in their respective fields.
Ensuring Compliance
Ensuring compliance with combustible dust safety guidelines is paramount for businesses looking to protect their workforce and assets. Staying compliant begins with a comprehensive understanding of the specific safety regulations pertinent to your industry, such as those set forth by OSHA and the National Fire Protection Association.
Regular dust hazard assessments and audits are essential for identifying and addressing potential risks. Implementing robust housekeeping measures to control dust accumulation and investing in employee training and awareness programs can significantly reduce the likelihood of incidents.
Additionally, staying updated with evolving safety standards from a national fire protection agency and technology is key to maintaining compliance over time. By prioritizing compliance and safety, businesses safeguard their operations that create dust and demonstrate a commitment to responsible practice.
The threat of combustible dust explosions is real but preventable with the right measures.
How to Manage Combustible Dust Safely:
Preventative Measures
Preventative measures are the foundation of effective combustible dust management, and they are also vital for combustible dust safety strategies. To mitigate the risks associated with combustible dust, implementing proactive techniques is essential.
Dust collectors and a dust collection systems are among the most crucial tools in this endeavor. These dust collectors and dust collection systems capture and remove dust particles from the air, preventing dust accumulation on suspended ceilings and the formation of an explosive cloud, or a catastrophic secondary explosion.
Additionally, employing proper ventilation, and using dust collectors, a dust collection system, and other dust collection equipment, are designed to minimize dust generation, and can further reduce the risk of ignition from an ignition source.
Regular equipment maintenance and inspections play a pivotal role in ensuring the continued effectiveness of preventive measures, along with education on the five factors (oxygen, heat, fuel, dispersion, and confinement) of the Dust Explosion Pentagon.
Emergency Preparedness
Emergency preparedness is a critical first step aspect of safeguarding your business against the potential devastation of a flash fire or combustible dust explosions, while also aligning with combustible dust hazard best practices.
To effectively respond to such incidents, it’s essential to have a well-defined emergency plan in place. This plan should encompass the installation and accessibility of emergency equipment such as fire extinguishers, sprinkler systems, and explosion venting devices.
Equally vital is the provision of comprehensive training for employees, ensuring they are well-versed in emergency procedures, evacuation routes, and the proper use of safety equipment.
By prioritizing emergency preparedness, businesses not only protect their workforce and assets but also send a clear message of responsibility and safety to their employees.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Maintenance and inspections in manufacturing processes are the linchpin of a robust combustible dust management strategy.
The importance of routine checks cannot be overstated, as they are instrumental in identifying a process that generates dust and preventing dust-related incidents. These inspections should encompass various critical components such as dust collection systems, dust collectors and dust capture equipment, and ventilation systems. Regularly assessing the condition of these systems, checking for wear and tear, hot surfaces, and ensuring they are in optimal working order is paramount.
Moreover, conducting dust hazard analyses at regular intervals to identify evolving risks is crucial. By prioritizing these maintenance and inspection practices, businesses not only enhance occupational safety but also convey a commitment to responsible practices, which resonates positively with the employees.

Conclusion
Combustible dust poses a serious risk, but with proper management, businesses can prevent catastrophic explosions. By implementing dust control measures, adhering to safety regulations, and training employees, workplaces can ensure a safer environment and protect lives and property.
It’s a win-win situation where safety and visibility go hand in hand, ensuring a secure and prosperous future and increased workplace safety from combustible dust fires and hazards.
About Dust Safety Science
Dr. Chris Cloney, of Dust Safety Science, provides additional Combustible Dust information, with a Podcast. Click on the latest Podcast Link: What is Combustible Dust and Combustible Dust Hazards.

Resources:
Visit Dust Safety Science (Global Incident Tracking)
Visit Dust Safety Academy (Resources, Training and Events)
Visit Dust Safety Professionals (Need Help? Get Support Today!)
Visit Dust Safety Journal for the Dust Safety Science Monthly Journal
Subscribe to our Dust Safety Science Newsletter at Dust Safety Science Newsletter
Visit the Dust Safety Science blog for written articles on combustible dust safety including the latest research, expert opinions, and state-of-the art in fire and explosion protection.
