Updated December 31, 2024 Authored by Dr. Chris Cloney and Jon Barrett of Dust Safety Science
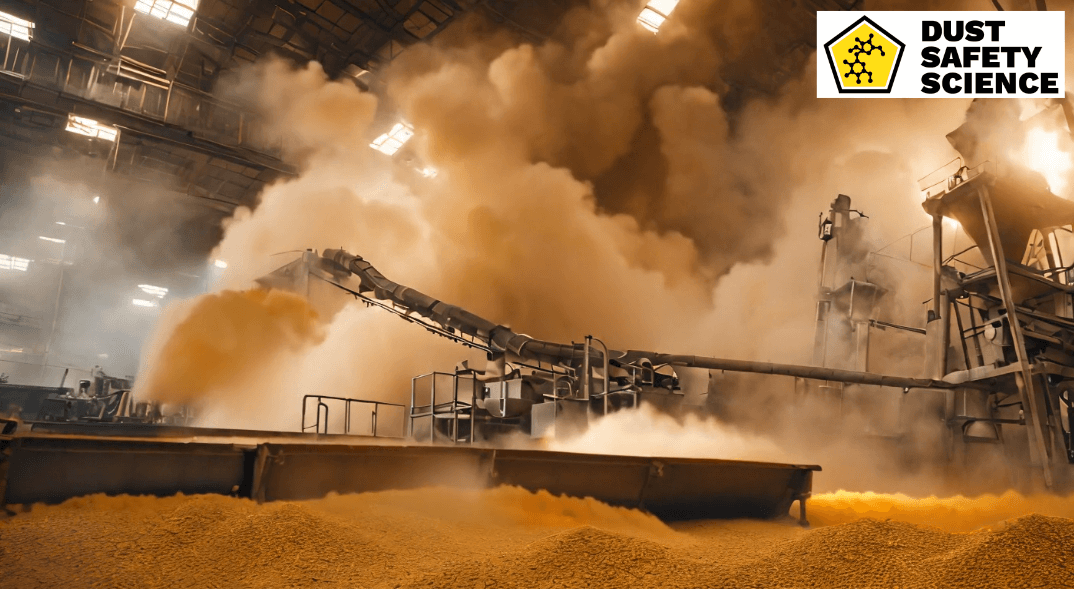

Introduction to Dust Suppression and Combustible Dust
In industrial settings, the omnipresent hazard of combustible dust and dust control is continuous, posing significant risks to safety, health, and the environment. From coal mines to manufacturing facilities handling organic materials, the threat of combustible dust explosions demands vigilant suppression measures. OSHA states that dust suppression is an engineering control for safety precautions with combustible dust. Specific types of combustible dust are encountered in various industries and tailored suppression solutions, and effective dust control methods, are essential for dust management and to prevent dust accumulation.
The NFPA 654 Standard for the Prevention of Fire and Dust Explosions from the Manufacturing, Processing, and Handling of Combustible Particulate Solids, provides guidance on combustible dust suppression and dust control. The NFPA 654 Standard is referenced by OSHA’s Combustible Dust National Emphasis Program (NEP) to identify dust hazards, dust control, and define mitigation strategies that help protect life and property. The standard provides industry-recognized safety practices for facility and systems design, process equipment protection, fugitive dust control and housekeeping, ignition source identification and control, fire protection, training and procedures, inspection, and maintenance. Annexes offer guidance on the application of area electrical classification for various dust accumulation levels.
Dust suppression and effective dust control methods encompass a diverse array of techniques aimed at controlling the dispersion of dust particulates, fugitive dust, dust levels, and dust formation in industrial environments and dust management. From mechanical barriers to chemical treatments and advanced filtration systems, these methods offer multifaceted approaches to addressing the unique challenges posed by combustible dust. Understanding the specific characteristics of combustible dust encountered in various industries is essential for tailoring effective suppression strategies. Of the various industrial hazards, few are as insidious and potentially catastrophic as a combustible dust explosion. This fine dust of various industrial processes poses a significant threat to safety, health, and the environment. Dust suppression emerges as a critical tool in mitigating these risks, as a dust control solution, by increasing air quality, and ensuring operational continuity.
Industrial Operations, Mining, and Construction Sites Creating Airborne Dust
Industrial operations across sectors such as manufacturing, agriculture, mining, and pharmaceuticals inevitably generate dust, increase dust levels, and require dust suppressants and dust suppression. While often viewed as a mere inconvenience, unchecked dust poses serious risks and hazards. Apart from its role as a respiratory irritant, certain types of dust—particularly those of organic or metallic origin—can combust when dispersed in the air in sufficient concentrations. Using a dust suppressant and dust suppression methods for fugitive dust thus becomes paramount not only for maintaining a clean and safe work environment but also for preventing catastrophic incidents.
Industrial dust isn’t merely a nuisance; it’s a silent menace with far-reaching implications. Inhalation of dust particles from fugitive dust can lead to respiratory ailments, while combustible dust presents an imminent fire and explosion hazard. Moreover, dust dispersion and dust mites can contaminate soil, water bodies, and air quality, posing ecological risks. Recognizing and addressing these implications with dust control and dust suppression solutions, is crucial for safeguarding human health and environmental integrity.
Dust suppression solutions such as dust suppression products and dust control methods represent a diverse array of techniques aimed at mitigating the risks associated with industrial dust. From mechanical barriers to chemical treatments, such as a dust suppressant, and advanced filtration systems, these methods offer a multifaceted approach to controlling dust emissions and minimizing associated hazards. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, (E.P.A.), dust control measures apply to any construction site where major soil disturbances or heavy equipment
construction activities—such as clearing, excavation, demolition or excessive vehicle traffic—occur.

A picture of the NFPA 654 Standard for the Prevention of Fires and Dust Explosions the Manufacturing, Processing, and Handling of Combustible Particulate Solids
Understanding Dust Suppression and Combustible Dust
Dust suppression entails the application of various measures to control the dispersion of dust particles in industrial settings with a dust suppress, ant. According to Wikipedia, dust abatement and dust control are similar to dust suppression. Dust suppressions’ significance lies in its ability to mitigate health and safety risks, ensure regulatory compliance, and protect the environment from the adverse effects of dust pollution. Managing combustible dust poses unique challenges due to its inherent flammability and explosiveness. Traditional dust suppression solutions and dust suppression methods may prove insufficient in containing such hazards, necessitating specialized approaches and equipment. Additionally, the dynamic nature of industrial processes, the diversity of dust types, and dust levels, further complicate effective dust management.
Key Components of Dust Suppression Systems
Effective dust suppression systems and dust control, incorporate several key components designed to address the specific hazards posed by combustible dust. These components may include dust suppression products, dust suppression agents, advanced application methods, air filtration and collection systems, physical barriers, and comprehensive monitoring mechanisms.
Dust suppression agents play a pivotal role in neutralizing combustible dust particles and preventing their dispersion. These chemicals are specially formulated to address the unique characteristics of combustible dust, including its flammability and explosiveness, for safe and proper dust suppression. Common types of dust suppression products and dust suppressants for combustible dust include wetting agents, foams, and specialized polymer solutions.
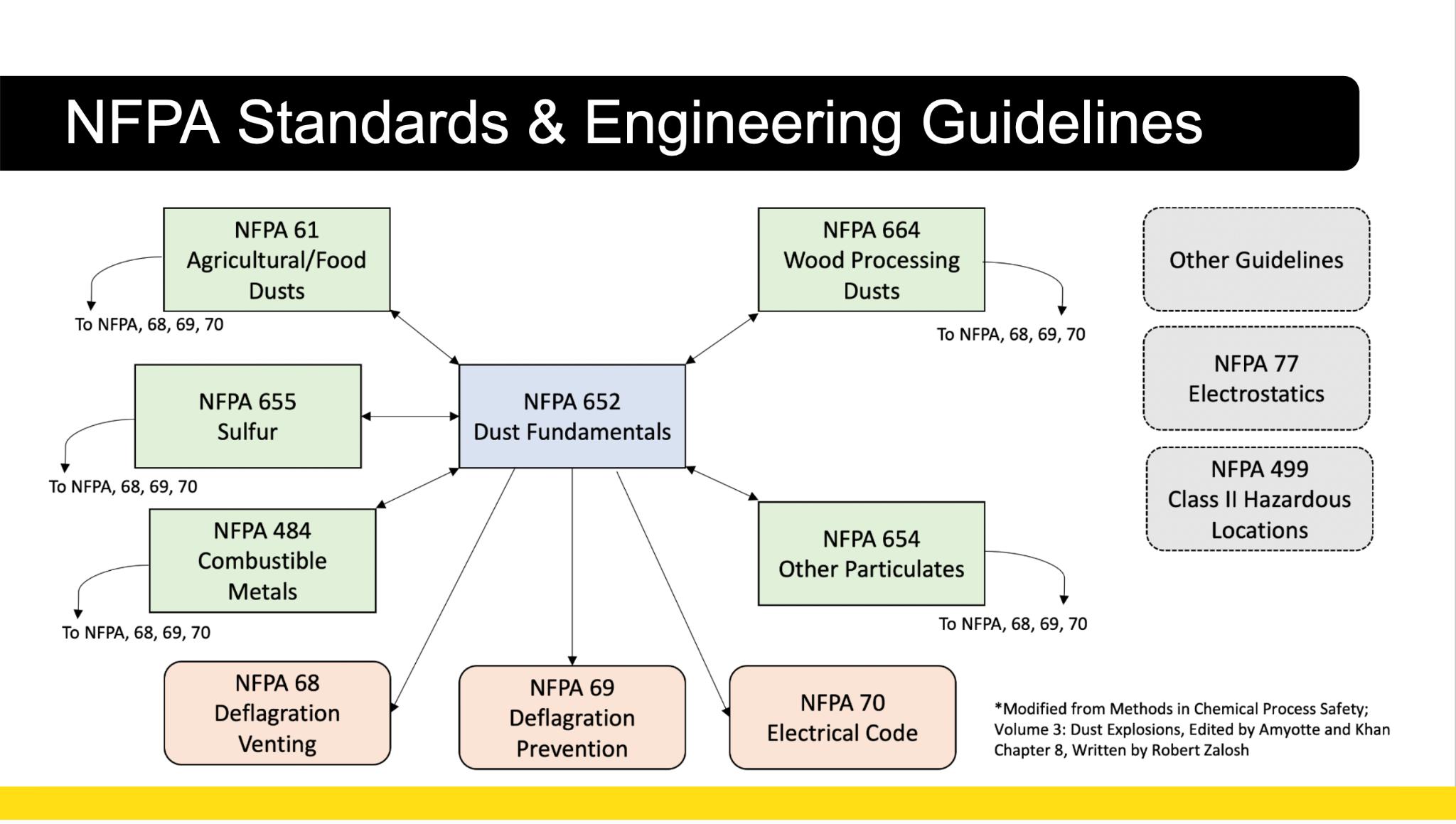
A picture of NFPA Publications Relevant to Combustible Dust Suppression and Dust Control
Advanced Dust Suppression Methods and Dust Control techniques
- Water Spraying Systems: Techniques and Technologies for Water-Based Dust Control
Water spraying systems and water trucks represent one of the primary dust suppressant methods for controlling combustible dust by binding particles together and reducing their flammability. Advanced techniques such as atomization and misting, (spray a fine mist of water and surface active agents to capture airborne dust particles and small airborne particles), and bring them to the ground. This will enhance the effectiveness of water based dust control, ensuring water barriers thorough coverage and saturation of dust-laden surfaces. Wet dust extraction entails designing and providing control solutions for handling and transferring coal, including crushing, screening, loading onto conveyor belts, and other related processes. Warning and Disclaimer: OSHA states do not use water as a preventive measure on such fuels, such as Combustible Metal Dust and certain types of dust and hazardous mixtures. OSHA also states the use of high pressure water sprays, can also disperse combustible dust into the air. Metal dust fires require Class D fire extinguishers and agents.
- High-Pressure Mist Systems
High-pressure mist systems using water, deliver finely atomized water droplets at high velocities to envelop combustible dust while controlling dust, and effectively suppressing their flammability and preventing potential ignition sources. These systems are particularly suited for enclosed or semi-enclosed environments where conventional spraying methods may be less effective. - Rain Gun and Sprinkler Systems
Rain guns and sprinkler systems using water, simulate natural rainfall by dispersing water over large areas, providing effective dust control in outdoor environments prone to combustible dust accumulation and preventing wind from allowing to blow loose soil particles and fine particles. These systems help control dust, reduce dust emissions, and mitigate the risks of fire and explosion by reducing dust concentrations and dampening potential ignition sources. A physical barrier, may be required to prevent standing water.
- Chemical Dust Suppressants: Types and Applications
Chemical dust suppression involves various methods that primarily use water to introduce specific chemicals at certain facility locations to suppress dust. Chemical dust suppressants offer targeted solutions for controlling combustible dust by modifying its physical and chemical properties to reduce its flammability and explosiveness. Wetting agents and surfactants as surface active agents enhance the wetting ability of water, ensuring thorough coverage and penetration of dust particles. Foam-based suppressants create a protective barrier that seals combustible dust, preventing its dispersion and reducing the risk of ignition and the process to absorb moisture. Highly refined synthetic fluids are the latest environmentally friendly dust control products which works through adsorption onto the treated surface, making dust particles heavy to be airborne. Vegetable oils such as soybean, cottonseed and canola oil are common dust control methods, and can be environmentally friendly, with vegetable oils applied in controlled, limited quantities. Organic materials such as calcium chloride and magnesium chloride, and synthetic polymer solutions form a cohesive film over dust surfaces, effectively encapsulating combustible particles and minimizing their reactivity. According to this ScienceDirect research study, Ammonium polyphosphate (APP) was often used to suppress dust explosions owing to its excellent thermal stability, high nitrogen, and phosphorus content, etc. It had been proven to have a well-suppression effect on the explosion of starch, sucrose dust, and other biomass dust.
- Air Filtration and Collection Systems: Capturing Dust Before it Spreads
In addition to suppressing dust at the source, effective dust control also involves capturing airborne particles before they disperse and pose a fire hazard. Air filtration and dust collection systems, including baghouse filters, electrostatic precipitators, and cartridge collectors with HEPA filters, play a crucial role in this regard by capturing combustible dust and preventing its escape into the surrounding environment.
- Physical Barriers and Containment Measures: Preventing Dust Dispersion
Preventing combustible dust dispersion is paramount in mitigating fire and explosion hazards. Physical barriers and containment measures such as hoods, and enclosures, help confine combustible dust to designated areas, allowing for removing dust from the area, minimizing its exposure to air currents and ignition sources and reducing the likelihood of catastrophic incidents.
Implementing Cost Effective and Efficient Dust Suppression Strategies, for Safety and Maintenance
Developing a cost effective dust suppression and dust control plan for combustible dust requires a systematic approach that takes into account the unique characteristics of the dust, the operational environment, and the specific hazards posed by combustible dust. Key steps include conducting a thorough risk assessment, identifying critical control points, selecting appropriate suppression methods to keep the particles together, and implementing comprehensive monitoring and maintenance protocols.
Identifying the sources of combustible dust and assessing the associated risks is essential for developing targeted suppression strategies. This involves analyzing the type and quantity of dust produced, evaluating potential ignition sources, and identifying areas where dust concentrations may pose a significant hazard.
Selecting the most suitable suppression methods and dust suppressant for combating combustible dust depends on various factors, including the type of dust, the operational environment, and regulatory requirements. It may involve a combination of techniques such as water spraying, chemical treatment, surface tension, air filtration, and physical barriers tailored to address specific hazards and operational constraints.
Comprehensive control of combustible dust often requires the integration of multiple suppression techniques to address the diverse challenges posed by its flammability and explosiveness. By combining methods such as water-based suppression, chemical treatment, and advanced filtration systems, organizations can effectively mitigate fire and explosion risks and ensure a safe working environment.
Maintenance and Monitoring of Dust Suppression Systems
Long term, regular maintenance of dust suppression systems is essential for ensuring their continued effectiveness and longevity. This includes inspecting equipment for wear and damage, cleaning filters and nozzles, replenishing chemical agents such as calcium chloride and magnesium chloride, and a synthetic polymer, using geotextile fabrics as a base cover. Conducting periodic performance checks to identify and address potential issues of the soils beneath.
Continuous monitoring and evaluation of dust suppression system and dust particle capture performance are critical for detecting any deviations from expected performance levels and implementing corrective actions as needed. This involves collecting data on dust levels, air quality, equipment operation, and compliance with regulatory standards and using this information to optimize system performance and maintain compliance.
Based on the data collected through monitoring efforts, organizations can make adjustments and optimizations to their dust suppression systems to enhance short term efficiency and effectiveness. This may involve fine-tuning spray patterns, adjusting chemical dosages, upgrading filtration systems, or implementing additional control measures to address emerging challenges and ensure ongoing compliance with safety and environmental regulations. In addition, erosion control at mining and construction sites, from unpaved roads and dirt roads with standing water, to road construction and vehicle wheels in fine soil, which may create dust. If the surface has minimal natural moisture, with a hard surface, it is recommended to pre-wet the surface with water, in order to reduce surface tension. Synthetic Polymer Emulsions dust suppressants are a type of dust control solution that can be used to increase the tensile strength of clay roads.
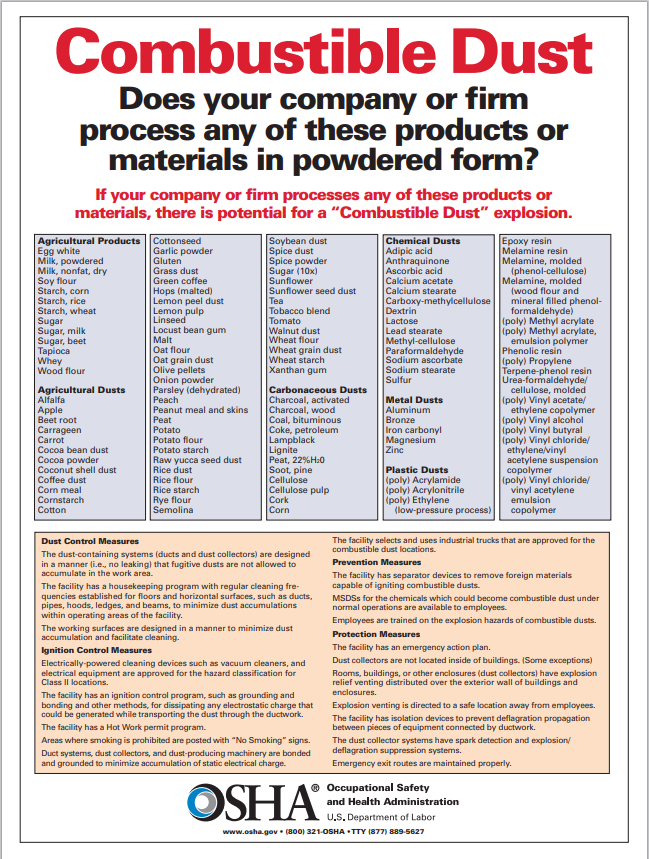
Conclusion
Combustible dust poses a significant fire and explosion hazard in industrial environments, and coal mining areas such as the Powder River Basin, construction sites, unpaved roads, dirt roads that produce dust, requiring proactive measures to mitigate risks and ensure worker safety and operational continuity. Cost efficient, cost effective, and environmentally friendly dust suppression solutions, dust control products, and synthetic polymers, to suppress and remove dust play a crucial role in controlling combustible dust, reduce dust and airborne particles, and minimizing associated hazards. By understanding the unique characteristics of combustible dust and implementing appropriate suppression strategies, and dust management, organizations can create safer working environments and reduce health hazards, and the likelihood of catastrophic incidents over a long period.
In the industrial landscape, dust can be a silent but potent adversary. Whether it’s airborne dust particles from manufacturing processes or loose dust particles stirred up by wind and traffic movements, the presence of dust can pose serious hazards to both health and safety. However, with the right dust control techniques, dust suppressant, and measures, it’s possible to effectively reduce dust, and manage and mitigate these risks.
Dust suppression is the process of controlling and reducing dust emissions to create a safer and healthier environment. It involves the use of various methods and dust suppression chemicals to suppress dust and reduce dust at its source. One of the primary objectives of dust suppression is to reduce airborne dust, which can be achieved by employing different dust control techniques and dust suppression products.
One effective approach to dust suppression is the use of dust suppressants, such as surface active agents or dust suppression chemicals like calcium chloride or highly refined synthetic fluids. These dust suppressant substances work by reducing the surface tension of water, allowing it to bind particles together, suppress dust, and reduce dust, and prevent them from becoming airborne. By applying dust suppressants to an unpaved roads, construction sites, and surfaces prone to dust resuspension, it’s possible to minimize its dispersal into the air.
Another strategy involves implementing dust control measures to directly target sources of dust emissions. This can include using barriers to block the spread of dust, installing ventilation systems to capture airborne dust, or employing techniques to stabilize loose soil particles and soil structure and prevent them from becoming airborne. For example, applying the dust suppressant calcium chloride to roads can help suppress dust by dampening the surface and preventing the formation of airborne fine particles.
Furthermore, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential components of effective dust suppression. By identifying potential sources of dust generation and implementing proactive measures to control dust, industries can significantly reduce the risks associated with dust exposure, and increase air quality.
About Dust Safety Science
For more from Dr. Chris Cloney on Combustible Dust Suppression, visit this podcast episode: How to Develop a Dust Control Project in a Coal Handling Process with Joe Finn.

Resources:
Visit Dust Safety Science (Global Incident Tracking)
Visit Dust Safety Academy (Resources, Training, and Events)
Visit Dust Safety Professionals (Need Help? Get Support Today!)
Visit Dust Safety Journal for the Complimentary, Dust Safety Science Monthly Journal
Subscribe to our Complimentary, Dust Safety Science Newsletter at Dust Safety Science Newsletter
Visit the Dust Safety Science blog for written articles on combustible dust safety including the latest research, expert opinions, and state-of-the-art in fire and explosion protection.
