Published September 17, 2024, Authored by Dr. Chris Cloney and Jon Barrett of Dust Safety Science

What Are Class 2 Division 2, Hazardous Locations?
Hazardous locations, as defined by the National Electrical Code (NEC), encompass areas where there is a risk of fire or explosion due to the presence defines hazardous locations as those areas where fire or explosion hazards may exist due to flammable gases or vapors, flammable liquids, combustible dust, or ignitable fibers, flakes, flock, or other agglomerating materials.
The National Fire Protection Association, (NFPA), NFPA 70 standard, and National Electrical Code, (NEC), are the standard for safe electrical design, installation, and inspection to protect people and property from electrical hazards.
One critical classification is Class 2 Division 2, which pertains to environments where combustible dust is not typically present during normal operations but can accumulate under abnormal conditions. Understanding the hazards specific to Class 2 Division 2 locations is essential to maintaining workplace safety, protecting employees, and adhering to regulatory compliance.
Definition and Criteria for Class 2 Division 2 Classification
Class 2 Division 2 hazardous locations are defined by combustible dust that can accumulate or become airborne, creating an explosive or flammable atmosphere under certain conditions. Unlike Division 1 areas, where combustible dust is present during normal operations, Division 2 locations only see dust buildup under abnormal conditions such as equipment malfunctions or poor housekeeping. Note that the dust must be present in sufficient quantities for a fire or explosion hazard to exist.
Key criteria include:
- Class 2: Pertains to combustible dust hazards.
- Division 2: Applies when the combustible dust is not normally present but may accumulate in quantities sufficient to cause an explosion or fire under abnormal operating conditions.
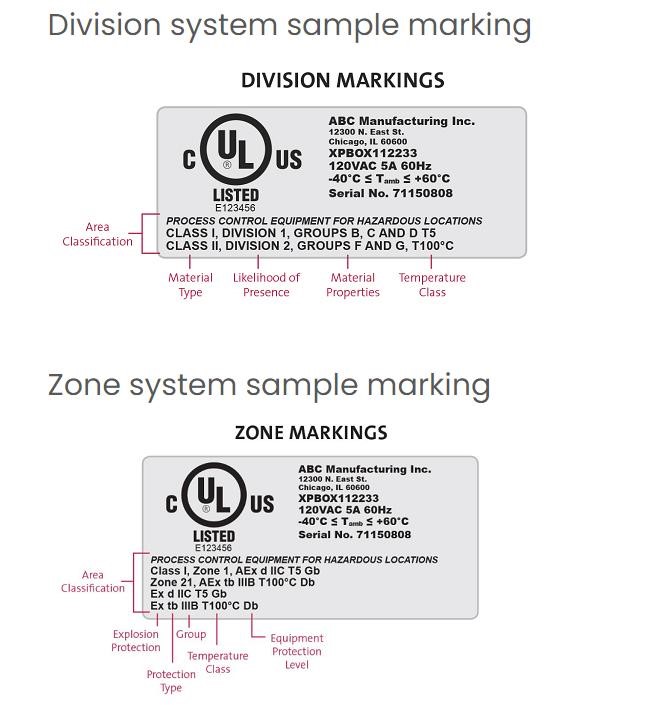
Area Classification: According to UL Solutions, hazardous locations are classified by the likelihood of an ignitable concentration of combustible material being present. There are two systems in place, including the traditional North American Division system and the alternative Zone system.
Examples of Class 2 Division 2 Environments, in Industries and Operations
Class 2 Division 2 environments and atmospheres can be found in a variety of industries that process, store, or handle materials prone to creating combustible dust. Common examples include:
- Grain handling and storage: Combustible dust from grains like wheat or corn can ignite if not managed properly.
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing: Powders used in drug production can create hazardous conditions if dust accumulates.
- Textile mills: Cotton dust can pose a fire risk in processing plants.
- Food processing plants: Dust from sugar, flour, and spices can present explosive risks.
The Role of Combustible Dust in Class 2 Division 2 Environments
Dust accumulation, particularly combustible dust, poses significant hazards that can lead to devastating explosions and fires. Understanding how to remove combustible dust from the air safely and effectively, is essential to protect workers, equipment, and the manufacturing facility.
Fine particles, such as combustible dust, can easily ignite and lead to dust explosions, which are often catastrophic. These combustible dust explosions occur when dust accumulates and becomes airborne, creating a dust cloud that can be ignited by heat sources, such as machinery, electrical sources, sparks, friction, or static electricity.
Class 2 Division 2 Requirements
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), UL Solutions, ATEX, and IECEx, provide standards and stringent guidelines for businesses operating in Class 2 Division 2 locations. These include requirements for:
- The National Fire Protection Association, (NFPA), NFPA 70 standard, and National Electrical Code, (NEC), the standard for safe electrical design, installation, and inspection to protect people and property from electrical hazards.
- NFPA 652 (Standard on Fundamentals of Combustible Dust): Outlines the basics of identifying, assessing, and managing combustible dust hazards.
- NFPA 654 (Standard for the Prevention of Fire and Dust Explosions from the Manufacturing, Processing, and Handling of Combustible Particulate Solids): Focuses on preventing fire and dust explosions in facilities where combustible dust is handled.
- OSHA’s Combustible Dust National Emphasis Program, (NEP): Highlights inspection and enforcement procedures to ensure businesses comply with safety requirements related to combustible dust.
- UL Solutions: UL and C-UL Hazardous Areas Certification for North America.
- (ATEX): Equipment for potentially explosive atmospheres. The ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU covers equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres, in the European Union.
- International Electrotechnical Commission System for Certification to Standards Relating to Equipment for Use in Explosive Atmospheres, (IECEx System): IEC 60079-10-2:2015 RLV is concerned with identifying and classifying areas where there are explosive dust atmospheres and combustible dust layers. The purpose of this standard is to allow for the proper assessment of ignition sources in these areas.
Compliance Obligations
Companies must implement comprehensive dust management programs, including regular housekeeping, equipment maintenance, and employee training, to mitigate risks in Class 2 Division 2 locations. Employers are responsible for identifying dust hazards, ensuring the installation of dust collection systems, and maintaining dust-tight enclosures for electrical equipment. Non-compliance with OSHA and NFPA standards can lead to citations, fines, and legal liabilities.
Legal Implications of Non-Compliance
Failure to meet the requirements set by OSHA or NFPA for Class 2 Division 2 locations can result in severe consequences, including:
- Fines and penalties: OSHA may issue hefty fines for non-compliance.
- Legal action: Companies could face lawsuits from injured employees or affected communities.
- Business shutdowns: Persistent non-compliance could result in temporary or permanent closures.
Dust-Proof and Explosion-Proof Equipment
Operating safely in Class 2 Division 2 locations requires specialized equipment designed to withstand the harsh conditions posed by combustible dust. Key equipment includes:
- Dust-tight enclosures: Electrical enclosures must be built to prevent dust ingress and avoid sparks that could ignite airborne particles.
- Explosion-proof motors and lighting fixtures: These safety features are essential to prevent electrical arcs or heat from igniting combustible dust.
- Grounding and bonding equipment: Properly grounded equipment helps prevent static electricity buildup, a common ignition source for dust explosions.
When selecting equipment for Class 2 Division 2 areas, it is essential to consider the following criteria:
- Temperature rating: Equipment must operate below the ignition temperature of the dust present.
- Ingress Protection (IP) rating: Choose equipment with a high IP rating to prevent dust from entering enclosures.
- Material compatibility: Equipment should be constructed from materials that resist corrosion and wear, especially in environments where abrasive or corrosive dust is present.
Assessing and Mitigating Risks in Class 2 Division 2 Locations
Effective risk management in Class 2 Division 2 locations involves regular assessment of dust hazards. This includes:
- Dust hazard analysis (DHA): Required by NFPA 652, a DHA identifies areas where combustible dust is present and evaluates potential risks.
- Monitoring dust levels: Install sensors and dust monitoring equipment to alert operators when dust levels reach dangerous thresholds.
- Regular housekeeping: Frequent cleaning is crucial to prevent dust accumulation, especially on high surfaces and hard-to-reach areas.
Implementing Dust Control Measures
Implementing dust control systems is a key step in reducing the risk of combustible dust explosions:
- Dust collection systems: These systems remove airborne dust particles and prevent them from accumulating on equipment or surfaces.
- Ventilation systems: Adequate ventilation ensures that dust is continuously removed from the environment and reduces the concentration of combustible dust in the air.
- Housekeeping Practices: Regular cleaning to minimize combustible dust accumulation.
- HazLoc and UL certified dust control fans: can play a role in handling combustible dust in industrial settings.
Safety Audits and Employee Training
Conducting routine safety audits ensures compliance with combustible dust safety standards and identifies potential areas of improvement. Additionally, employees must be trained in hazard recognition, proper equipment use, and emergency procedures.
Real-World Incidents in Class 2 Division 2 locations
Several high-profile incidents in Class 2 Division 2 locations have highlighted the need for strict safety protocols. One example is the 2008 sugar dust explosion at the Imperial Sugar refinery in Georgia, which resulted in 14 deaths and numerous injuries. This tragic incident underscores the importance of dust control and proper safety measures in preventing disasters.
Technology Advances, with the Integration of Artificial Intelligence, (AI), and Machine Learning, (ML), in Class 2 Division 2 Hazardous Locations
Technological advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming safety management in Class 2 Division 2 hazardous locations. AI-driven systems, combined with IoT sensors, can continuously monitor dust levels, temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions in real time. This technology enables businesses to detect abnormal conditions before they escalate into hazardous situations. For example, IoT-connected dust sensors can provide continuous data on particulate levels, allowing AI algorithms to identify patterns, predict potential dust explosions, and trigger automatic alerts or shut down systems to prevent incidents.
Machine Learning enhances these capabilities by analyzing historical data from Class 2 Division 2 environments and improving predictive models over time. ML algorithms can identify previously unnoticed correlations between different risk factors, providing more accurate risk assessments and allowing companies to implement more effective preventive measures. Additionally, these technologies help optimize maintenance schedules by predicting when equipment failures might occur, reducing the likelihood of malfunction-related dust accumulation. Together, AI, IoT, and ML are creating smarter, more proactive safety management systems, reducing human error, and enhancing overall workplace safety in hazardous environments.
FAQ Section
What defines a Class 2 Division 2 hazardous location?
A Class 2 Division 2 hazardous location is an area where combustible dust is present under abnormal conditions, such as equipment malfunctions, but is not usually part of regular operations.
What equipment is required for Class 2 Division 2 areas?
Essential equipment includes dust-tight enclosures, explosion-proof lighting, and properly grounded systems to prevent static electricity buildup.
How can businesses comply with OSHA and NFPA standards?
Compliance involves conducting a dust hazard analysis, maintaining dust control systems, and regularly training employees on dust safety and emergency procedures.

Conclusion
Class 2 Division 2 hazardous locations present significant risks due to combustible dust. However, with the right equipment, rigorous safety protocols, and ongoing employee training, businesses can maintain safe and compliant operations. Adhering to OSHA, NFPA, UL Solutions, ATEX, and IECEx, standards not only ensures legal compliance but also protects workers and the facility from potentially catastrophic incidents.
By investing in high-quality dust-proof equipment, implementing effective risk management strategies, and maintaining up-to-date emergency response plans, businesses can minimize the risks associated with Class 2 Division 2 environments.
About Dust Safety Science
Dr. Chris Cloney, of Dust Safety Science, provides additional information on Hazardous Area Classification Assessment for Combustible Dust, with a Podcast. Click on the latest Podcast Links: Steps to Completing a Hazardous Area Classification Assessment for Combustible Dust

Resources:
Visit: Fire and Explosion Protection Equipment Providers
Visit: Risk Assessment & Dust Hazard Analysis Providers
Visit: Combustible Dust Testing Providers
Visit Dust Safety Science (Global Incident Tracking)
Visit Dust Safety Academy (Resources, Training, and Events)
Visit Dust Safety Professionals (Need Help? Get Support Today!)
Visit Dust Safety Journal for the Dust Safety Science Monthly Journal
Subscribe to our FREE, Dust Safety Science Newsletter at Dust Safety Science Newsletter
Visit the Dust Safety Science blog for written articles on combustible dust safety including the latest research, expert opinions, and state-of-the art in fire and explosion protection.
